Anesthesia machines are like silent heroes in the operating room. They work quietly to keep patients safe, asleep, and pain-free during surgery. These machines are essential for making sure surgeries go smoothly. But what are anesthesia machines, and how do they work? Let’s explore what they do, their parts, and how they help improve healthcare.
What Is an Anesthesia Machine?
An anesthesia machine is a special medical device that helps patients stay asleep and safe during surgery. It delivers the right mix of oxygen and anesthetic gases to keep them stable. Think of it as a lifeline that supports patients while surgeons do their work. The machine carefully controls and monitors the gases, making sure the patient stays asleep and their breathing and heart rate are steady.
The Function of Anesthesia Machines

Anesthesia machines have one main job: to keep patients safely asleep and pain-free during surgery. But they do much more than that! Here’s a simple breakdown of their functions:
Delivering Oxygen and Anesthetic Gases
The machine provides a mix of oxygen and anesthetic gases, like nitrous oxide, to keep the patient sedated and pain-free while ensuring they get enough oxygen.
Helping with Breathing
If needed, the machine can breathe for the patient, keeping their airways open and making sure they get enough oxygen throughout the procedure.
Monitoring Vital Signs
The machine keeps track of important signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. This helps the medical team quickly spot and fix any problems.
Ensuring Safety with Pressure Control
It has safety features like pressure relief valves and alarms to prevent issues like too much pressure in the system, protecting both the patient and the medical staff.
Gas Flow Through an Anesthesia Machine
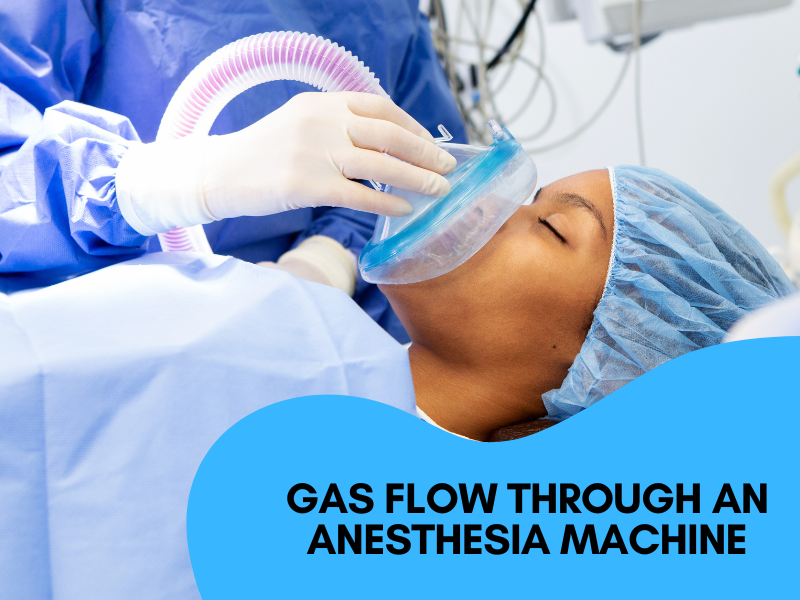
One of the most crucial aspects of anesthesia machines is the delivery of gases. The flow of gases follows a carefully orchestrated path that ensures the patient receives the right mixture at the right pressure. Here’s a simplified guide to gas flow:
Oxygen Supply
Medical-grade oxygen enters the machine either from a central pipeline or an oxygen tank. This is the foundation of the patient’s anesthetic mixture.
Flowmeters and Vaporizers
The oxygen passes through flowmeters, which measure the volume of gas flowing to the patient. From there, the oxygen enters the vaporizer, where volatile anesthetic agents are added. These vaporizers convert liquid anesthetic agents into a gas form, ensuring that the patient receives the correct concentration of anesthesia.
Common Gas Outlet
Once mixed, the oxygen-anesthetic mixture travels to the common gas outlet, where it is delivered to the patient through a mask or endotracheal tube.
Exhalation and Scavenging
As the patient exhales, the gases are directed back into the circuit. Waste gases are then safely removed through a scavenging system. This system prevents environmental contamination and protects the medical team from exposure to residual anesthetic agents, a critical safety feature of anesthesia machines.
Key Components of an Anesthesia Machine

Anesthesia machines have several important parts that work together to keep patients safe and comfortable during surgery. Here’s a simple guide to what each part does:
Oxygen and Gas Supply
The machine gets oxygen from a tank or the hospital’s oxygen system to deliver it to the patient.
Flowmeters
These control how much oxygen and other gases flow to the patient, making sure the right amount is delivered.
Vaporizer
This part changes liquid anesthesia into gas and mixes it with oxygen to give the patient the correct dose.
Breathing Circuit
The breathing circuit includes tubes and connectors that send the anesthetic gas to the patient and carry the exhaled gas back to the machine.
Pressure Relief Valve
This safety valve keeps the gas pressure in the system at a safe level to protect the patient.
Scavenging System
This system removes leftover gases from the machine, keeping the operating room air safe to breathe.
Ventilator
If the patient can’t breathe on their own, the ventilator takes over, helping them get the oxygen they need.
Monitoring and Alarms
The machine tracks the patient’s vital signs, like heart rate and oxygen levels. If something is wrong, alarms let the medical team know right away.
Anesthesia Circuits: Different Options for Different Needs

The Anesthesia Circuits play a crucial role in delivering gases to the patient and removing waste gases. Depending on the patient’s condition and the type of procedure, different circuits may be used:
- Mapleson Circuit: Ideal for pediatric patients or situations requiring spontaneous breathing, this circuit uses a high-flow of fresh gases to eliminate exhaled carbon dioxide.
- Semi-Closed Circuit: This system allows for the partial rebreathing of exhaled gases, conserving oxygen while maintaining an adequate flow of anesthetic agents. It’s typically used in adult patients for general anesthesia.
- Closed Circuit: In this circuit, the patient breathes almost entirely exhaled gases, with only a small amount of fresh gas added to replace the consumed oxygen. This method is highly efficient, though it requires careful monitoring.
- Circle Circuit: Often used in modern operating rooms, this circuit allows for a mix of rebreathing and fresh gas delivery, offering a balance of efficiency and patient safety.
An anesthesia machines is essential in managing these circuits, ensuring the appropriate delivery of gases during surgery.
Common Issues and Concerns with Anesthesia Machines

While anesthesia machines are robust and reliable, several challenges can arise that require close attention from medical professionals. These include:
Machine Malfunction
Like any mechanical system, anesthesia machines can fail. Regular maintenance and calibration are crucial to avoid mishaps, such as incorrect gas flow or pressure buildup.
Leaks in the Breathing Circuit
Leaks can lead to a loss of anesthetic gases, potentially endangering the patient’s safety. Proper sealing and routine checks help minimize this risk.
Contamination
Contaminants in the oxygen supply or anesthetic vapors can pose health risks to both patients and healthcare providers. Ensuring that gas supplies are free from impurities is essential.
Incorrect Settings
Setting the wrong gas concentration, pressure, or flow rate can lead to serious complications. This is why the healthcare team needs to be well-trained in operating the machines.
Waste Gas Exposure
Anesthetic gases can have harmful effects on operating room staff if not properly scavenged. Ensuring that the scavenging system is functioning well is essential for workplace safety.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes

Anesthesia machines aren’t just about the equipment—they also help the healthcare team work better together. Here’s how:
Real-Time Monitoring for Quick Action
These machines keep track of the patient’s vital signs, like heart rate and oxygen levels, in real-time. This helps the team make quick adjustments when needed.
Improved Team Communication
When the anesthesia machine is working properly, it makes things smoother for the anesthesiologist, surgeon, and other team members, helping them stay on the same page and provide better care.
Safety and Peace of Mind
With safety features like alarms and pressure controls, the team can focus on the surgery without worrying about equipment problems.
Saving Resources
By using gases and anesthesia efficiently, these machines save money while still keeping patients safe and comfortable.
Conclusion
Anesthesia machines are super important for keeping patients safe and comfortable during surgeries. They control and monitor the gases that help put patients to sleep. When used correctly, these machines protect patients and help the medical team work smoothly together. Fixing any issues and using the machines properly can make surgeries safer and improve patient care.
For expert support with medical equipment, visit Syracuse Biomedical Services.

