What is a Bone X-ray?

Common Applications of Bone X-rays
Bone X-rays are versatile and are used to diagnose and monitor a variety of conditions:- Detecting Fractures: X-rays are the primary tool for identifying broken bones, whether from accidents, falls, or other injuries.
- Diagnosing Joint Issues: They help identify problems with joints, such as arthritis, dislocations, or alignment issues.
- Evaluating Bone Health: X-rays are used to assess bone density and detect conditions like osteoporosis or bone infections.
- Guiding Treatment: X-rays can assist in planning surgical procedures or monitoring the healing process of bones.
Preparing for a Bone X-ray
Preparation for a bone X-ray is generally straightforward:- Wear Comfortable Clothing: You might need to change into a hospital gown if your clothes have metal fasteners. This is to avoid interference with the X-ray images.
- Remove Jewelry and Metal Objects: Metal can obscure the images, so it’s important to remove any jewelry or other metal objects near the area being examined.
- Inform the Technician: Let the X-ray technician know if you are pregnant or might be pregnant. X-rays are usually avoided during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary.
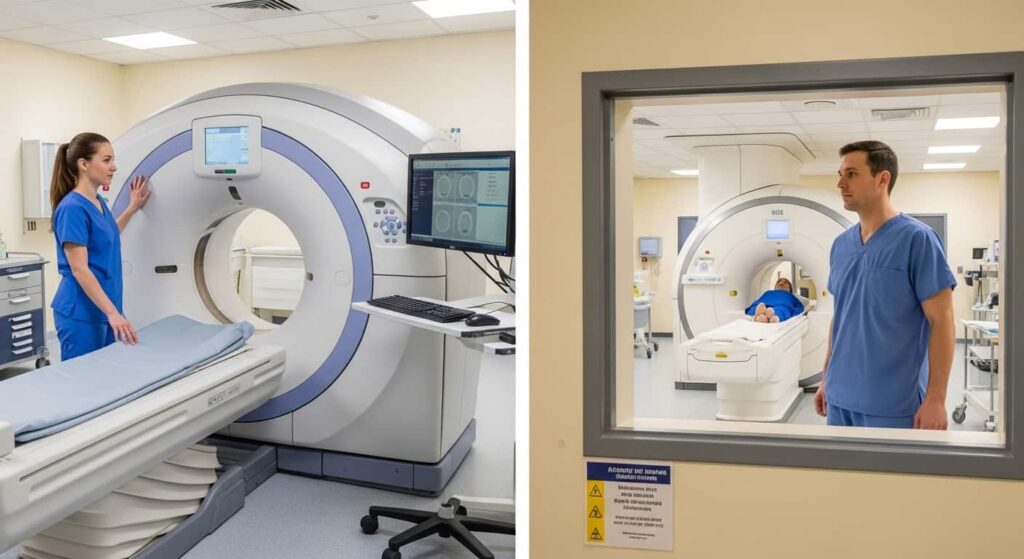
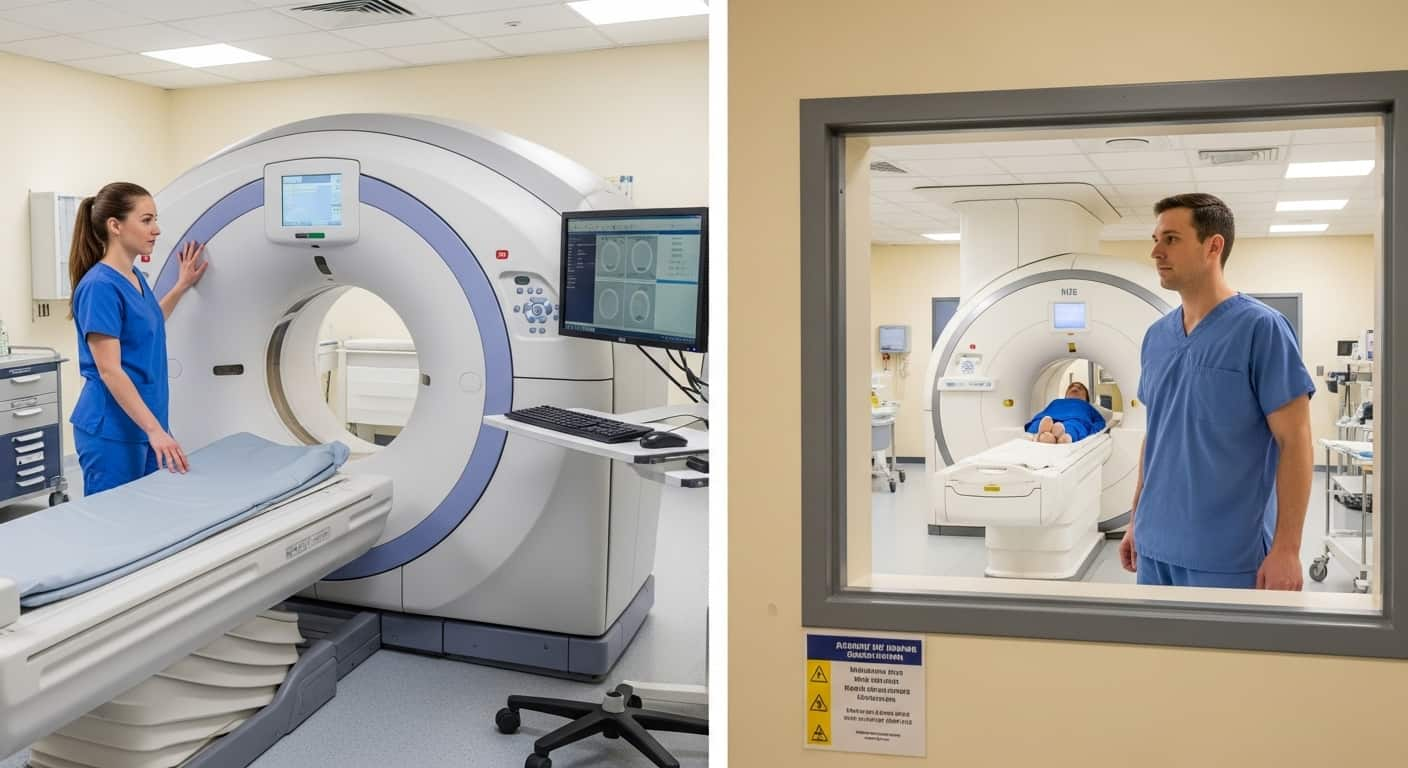
What Does the X-ray Equipment Look Like?
The equipment used in a bone X-ray includes:- X-ray Machine: This is a large device that sends X-rays through your body. It typically consists of a tube that directs the X-rays and a plate or sensor that captures the images.
- Image Receptor: The receptor, which can be a film or a digital detector, captures the X-ray images. It is positioned opposite the X-ray tube.
- Control Panel: The technician uses this panel to operate the X-ray machine, adjust settings, and capture the images.
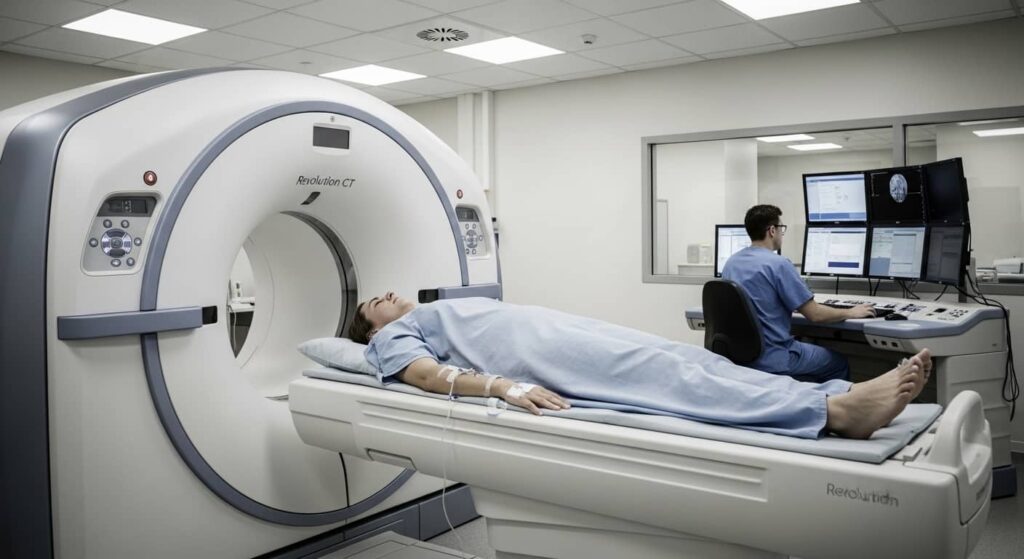
How the Bone X-ray Procedure Works

- Positioning: You will be positioned in front of the X-ray machine so that the area of interest is aligned properly. This may involve standing, sitting, or lying down, depending on which bone is being examined.
- Image Capture: The X-ray machine will be activated, sending a small amount of radiation through your body. The radiation passes through the bones and is captured by the image receptor. Dense materials like bones absorb more radiation and appear white on the image, while softer tissues absorb less and appear darker.
- Completion: Once the images are taken, you can get dressed and resume your normal activities. The entire process usually takes only a few minutes.
What to Expect During and After the X-ray
During the X-ray:- Holding Still: You may need to hold still and possibly change positions to get clear images.
- No Pain: The X-ray procedure is painless. The most you might experience is some discomfort from holding a position.
- Resuming Normal Activities: There is no recovery time required. You can return to your daily activities immediately.
- Receiving Results: The X-ray images will be reviewed by a radiologist, a specialist in reading medical images. They will send a report to your doctor, who will discuss the results with you.
Who Reads the Results and How to Get Them
A radiologist, a doctor trained to interpret X-ray images, will analyze the results. They prepare a detailed report on their findings, which is then sent to your primary care doctor or specialist. Your doctor will explain the results to you and recommend any further steps or treatments if needed.Benefits and Risks of Bone X-rays

Benefits
- Quick and Non-Invasive: The procedure is fast and does not require any invasive techniques.
- Detailed Bone Images: Provides clear and detailed images of bone structures, crucial for diagnosing and managing bone conditions.
- Essential for Diagnosis: Critical for detecting fractures, joint issues, and other bone-related conditions.
Risks
- Radiation Exposure: Although the amount of radiation used is minimal, there is a slight risk, particularly with frequent X-rays or during pregnancy. The benefits of the procedure generally outweigh the risks.
Limitations of Bone X-rays
Bone X-rays have certain limitations:- Limited to Bones: X-rays are excellent for viewing bones but do not provide detailed images of soft tissues like muscles, ligaments, or organs.
- Potential for Missed Details: Some subtle fractures or conditions may not be visible on X-rays, requiring additional imaging techniques like CT scans or MRIs for a more comprehensive view.
Other Types of Medical X-Ray
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Bone X-rays
-
1. Is a bone X-ray safe?
Yes. The radiation exposure from a bone X-ray is very small. For most people, the benefits of accurate diagnosis outweigh the minimal risk. However, if you are pregnant, inform your doctor or technician before the procedure.
-
2. How long does a bone X-ray take?
The procedure usually takes only a few minutes. The most time is spent positioning the body correctly.
-
3. Will a bone X-ray hurt?
No. The procedure itself is painless. You may feel some discomfort if you need to hold a specific position for a short time.
-
4. Do I need to prepare in advance?
Generally, no special preparation is needed. You may be asked to remove jewelry, metal objects, or change into a gown to avoid interference with the images.
-
5. When will I get my results?
A radiologist will analyze the images and send a report to your doctor. Your doctor will then share the results and next steps with you. This can take anywhere from the same day to a few days, depending on the facility.
-
6. Can an X-ray show all bone problems?
Not always. X-rays clearly show fractures, joint issues, and bone conditions, but may miss very small fractures or problems in soft tissues like muscles or ligaments. In those cases, other imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs may be recommended.
-
7. How often can I safely have an X-ray?
There’s no strict limit, but doctors avoid unnecessary X-rays. The radiation dose is very low, but repeated exposure should be minimized unless medically necessary.
-
8. What’s the difference between a bone X-ray and other X-rays (like dental or chest X-rays)?
The principle is the same, but the focus differs:
Bone X-ray: Looks at bones and joints for fractures, arthritis, or infections.
Dental X-ray: Examines teeth, gums, and jawbone health.
Chest X-ray: Checks lungs, heart, and chest bones.
-
9. Who performs the X-ray?
A trained radiologic technologist (X-ray technician) performs the procedure. The images are then reviewed by a radiologist, who sends the findings to your doctor.
-
10. Can children have bone X-rays?
Yes. Bone X-rays are safe for children and are often used to detect fractures or monitor growth. Extra care is taken to use the lowest radiation dose possible.