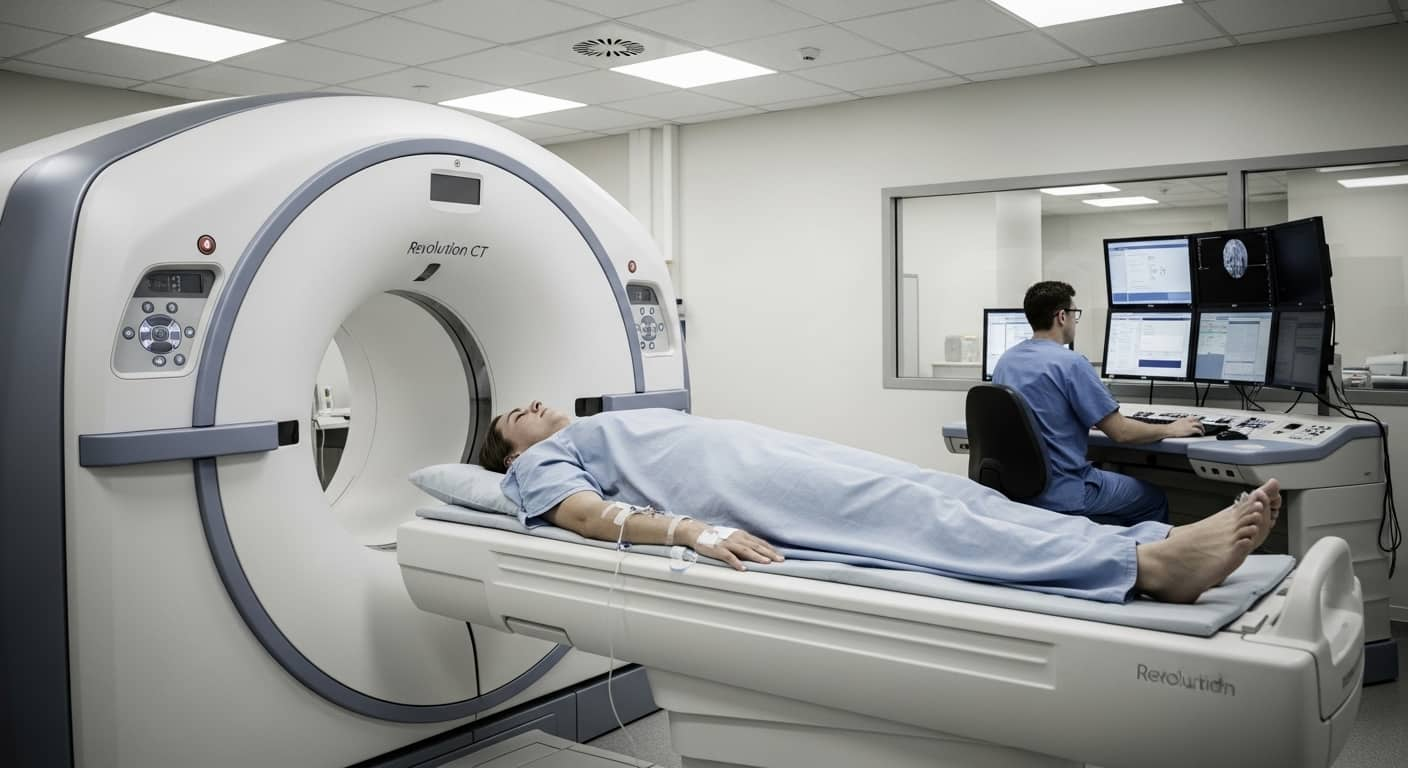
Have you ever wondered how doctors can see inside your body without making a single cut? That’s all thanks to medical imaging! This fantastic technology allows doctors to diagnose, treat, and monitor diseases by creating detailed images of the inside of our bodies. Together with SYB, we’re going to dive deep into what medical imaging is, its history, the different types of imaging techniques, and why it’s so important in healthcare.
What is Medical Imaging?

So, what exactly is medical imaging? In simple terms, it’s a way to create pictures of the inside of our bodies using different forms of energy like X-rays, sound waves, or magnetic fields. These images help doctors see what’s going on without surgery, which makes diagnosing and treating diseases a whole lot easier.
A Quick Trip Down Memory Lane: The History of Medical Imaging
Early Discoveries and Innovations
The story of medical imaging starts way back in 1895 when a guy named Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen accidentally discovered X-rays. This was a game-changer because, for the first time, doctors could see bones and other structures inside the body without cutting it open.
Evolution Over the Decades
Since then, medical imaging has come a long way. In the 1970s, CT scans were invented, providing even more detailed images. Then, in the 1980s, MRIs came along, giving doctors incredible views of soft tissues like the brain and muscles without using any harmful radiation.
Types of Medical Imaging Techniques
Let’s look at some of the different types of medical imaging techniques used today.
X-ray Imaging
X-rays are probably the most well-known type of medical imaging. They work by passing X-ray beams through the body. Bones absorb these beams and appear white on the image, while softer tissues look darker. X-rays are great for spotting broken bones, infections, and other bone-related issues.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
CT scans are like supercharged X-rays. They take multiple X-ray images from different angles and combine them to create detailed cross-sectional pictures of the body. This makes them really useful for diagnosing problems in the chest, abdomen, and pelvis, as well as spotting cancers and injuries from accidents.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is a bit different because it uses strong magnets and radio waves instead of X-rays. This technique is fantastic for getting detailed images of soft tissues like the brain, spinal cord, and muscles. Since MRIs don’t use radiation, they’re safer for repeated use. Doctors often use MRIs to diagnose things like brain injuries, spinal cord issues, and joint problems.
Ultrasound Imaging
You’ve probably heard of ultrasound because it’s commonly used during pregnancy to check on the baby. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It’s not just for pregnancy, though – doctors also use it to look at the heart, blood vessels, and other organs.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans
PET scans are a bit different from the others because they use a small amount of radioactive material to show how tissues and organs are working. This is especially helpful for detecting cancer and monitoring how it’s responding to treatment. PET scans can also be used to study brain function and diagnose conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
Other Imaging Techniques
There are several other specialized imaging techniques out there, too:
- Fluoroscopy: This technique uses continuous X-rays to create real-time moving images, often used during procedures like catheter insertions.
- Mammography: A specialized type of X-ray used to detect breast cancer.
- Nuclear Medicine Imaging: This involves using small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose and treat diseases, including single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and PET.
The Role of Medical Imaging in Diagnosis

Early Detection of Diseases
One of the biggest benefits of medical imaging is that it can help detect diseases early on. For example, mammograms can find breast cancer before it causes any symptoms, and CT scans can catch lung cancer in its early stages. Early detection means treatments can start sooner, which often leads to better outcomes.
Accuracy and Precision in Diagnosis
Medical imaging techniques are incredibly accurate and precise, which helps doctors make correct diagnoses without needing to perform invasive surgeries. High-resolution images from MRIs or CT scans provide detailed information about abnormalities, making it easier to diagnose complex conditions like brain tumors or heart diseases.
Medical Imaging in Treatment Planning and Monitoring
Pre-Treatment Planning
Medical imaging isn’t just for diagnosing diseases – it’s also crucial for planning treatments. Detailed images help surgeons understand exactly where a problem is and how extensive it is, which means they can perform more precise and less invasive surgeries. For instance, CT scans and MRIs are used to map out tumors before surgery or radiation therapy, ensuring that healthy tissues are spared as much as possible.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
Doctors also use imaging to keep track of how well treatments are working. Regular scans can show if a tumor is shrinking in response to chemotherapy or if a heart condition is improving after surgery. This helps doctors make informed decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop a treatment.
Technological Advancements in Medical Imaging
Digital Imaging and Telemedicine
The shift from analog to digital imaging has made a huge difference in healthcare. Digital images are clearer and can be easily stored, shared, and analyzed. This means doctors can collaborate more effectively, and telemedicine has become a reality. With telemedicine, specialists can review images and provide consultations without the patient needing to travel.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing medical imaging. These technologies can analyze images faster and sometimes more accurately than humans. For example, AI algorithms can spot lung nodules in CT scans or detect diabetic retinopathy in eye images, helping doctors diagnose diseases earlier and more accurately.
Challenges and Limitations
Technical and Operational Challenges
While medical imaging is incredibly powerful, it’s not without its challenges. Some imaging techniques might not provide enough detail or contrast to detect very small or subtle abnormalities. Also, artifacts (errors in images caused by patient movement or technical issues) can make it hard to interpret some images. Cost and accessibility are other big challenges, as advanced imaging technology can be expensive and not always available in low-resource settings.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Medical imaging also raises ethical and privacy issues. Techniques that use radiation, like X-rays and CT scans, pose some health risks, especially if used frequently. There are also concerns about patient privacy and data security because digital images can be vulnerable to unauthorized access.
The Future of Medical Imaging
Emerging Technologies
The future of medical imaging looks bright, with several exciting technologies on the horizon:
- 3D and 4D Imaging: These advancements provide more detailed and dynamic views of the body’s structures and functions.
- Hybrid Imaging: Combining different imaging methods, like PET-CT or PET-MRI, offers comprehensive insights by integrating anatomical and functional information.
- Molecular Imaging: This emerging technology aims to visualize molecular and cellular processes in real-time, potentially enabling earlier detection and personalized treatment of diseases.
Potential Improvements
Researchers are constantly working to improve current imaging techniques. This includes enhancing image quality, reducing radiation exposure, and developing more portable and cost-effective imaging devices. AI and machine learning are also expected to further refine image analysis and interpretation, making diagnoses faster and more accurate.
Conclusion

Summary of Key Points
Medical imaging is a cornerstone of modern healthcare, providing crucial insights into the body’s internal structures and functions. From early discoveries like X-rays to advanced techniques like MRI and PET scans, medical imaging has come a long way, greatly enhancing our ability to diagnose, treat, and monitor diseases.
Closing Thoughts
As technology continues to advance, the field of medical imaging will undoubtedly see further improvements, making healthcare more precise, personalized, and accessible. Staying informed about these advancements is essential for both healthcare providers and patients, as it ensures that we can leverage the full potential of medical imaging to improve health outcomes.
You Might Also Like:
- Revolutionize Your Healthcare: 7 Reasons Why You Need Biomed in Your Equipment Purchases
- Exploring Medical Equipment Inspection Requirements
- Common Biomedical Equipment
- Comprehensive Guide To Surgical Instruments Maintenance and Care
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is medical imaging?
Medical imaging is the process of creating visual images of the inside of the body to help doctors diagnose, monitor, and treat medical conditions.
2. Why is medical imaging important in healthcare?
Medical imaging allows healthcare providers to see internal organs, tissues, and bones without surgery, helping them detect diseases and guide treatment plans.
3. What are common types of medical imaging?
Common types include X‑rays, CT scans, MRI scans, ultrasound, and PET scans, each used for different diagnostic purposes.
4. Is medical imaging safe for patients?
Most medical imaging procedures are safe when performed properly, and healthcare providers carefully manage radiation exposure and other risks.
5. Who performs medical imaging procedures?
Medical imaging procedures are typically performed by trained radiologic technologists and interpreted by radiologists who specialize in diagnosing medical conditions through imaging.